python의 with문의 동작을 Context Manager와 함께 알아본다.
개요
python을 통해 file 읽기 쓰기를 할 때 open 함수를 with문을 통해서 사용하는 예제를 볼 수 있다. with문을 사용하면 close()를 자동으로 해준다라는 설명도 봤을 것이다.
open 함수가 with문에서 어떻게 동작하는지에 대해서 알아보자.
open 함수
with를 사용하지 않을 때,
1
2
3
4
5
file = open('./test.txt', 'w')
try:
file.write('hello')
finally:
file.close()
with를 사용할 때,
1
2
with open('./test.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write('hello')
Context Manager
Context Manager는 with 구문을 실행 할때, 진입과 종료시에 원하는 동작(runtime context)를 정의하고 실행한다.
__enter__ : with 구문에 진입되는 시점에 실행
__exit__ : with 구문에서 빠져나오기 전에 실행
class에 __enter__, __exit__ 함수를 구현하고, with 구문을 통해 실행하면 원하는 동작을 제어 할 수 있다.
아래 예시는 MyOpen이라는 class를 만들어서 open 함수를 한번 더 wrapping한 예제이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
class MyOpen():
def __init__(self, file_name, method):
self.io_wrapper = open(file_name, method)
def __enter__(self):
return self.io_wrapper
def __exit__(self, exc_type, value, trace_back):
if exc_type:
print(exc_type, value, trace_back)
self.io_wrapper.close()
1
2
with MyOpen('./test.txt', 'w') as f
f.write('hello')
open 함수가 with구문에서 동작할 수 있는 이유
open 함수를 실행하면 TextIOWrapper class의 인스턴스를 반환한다.
1
2
>>> open('./test.txt', 'w')
<_io.TextIOWrapper name='./test.txt' mode='w' encoding='UTF-8'>
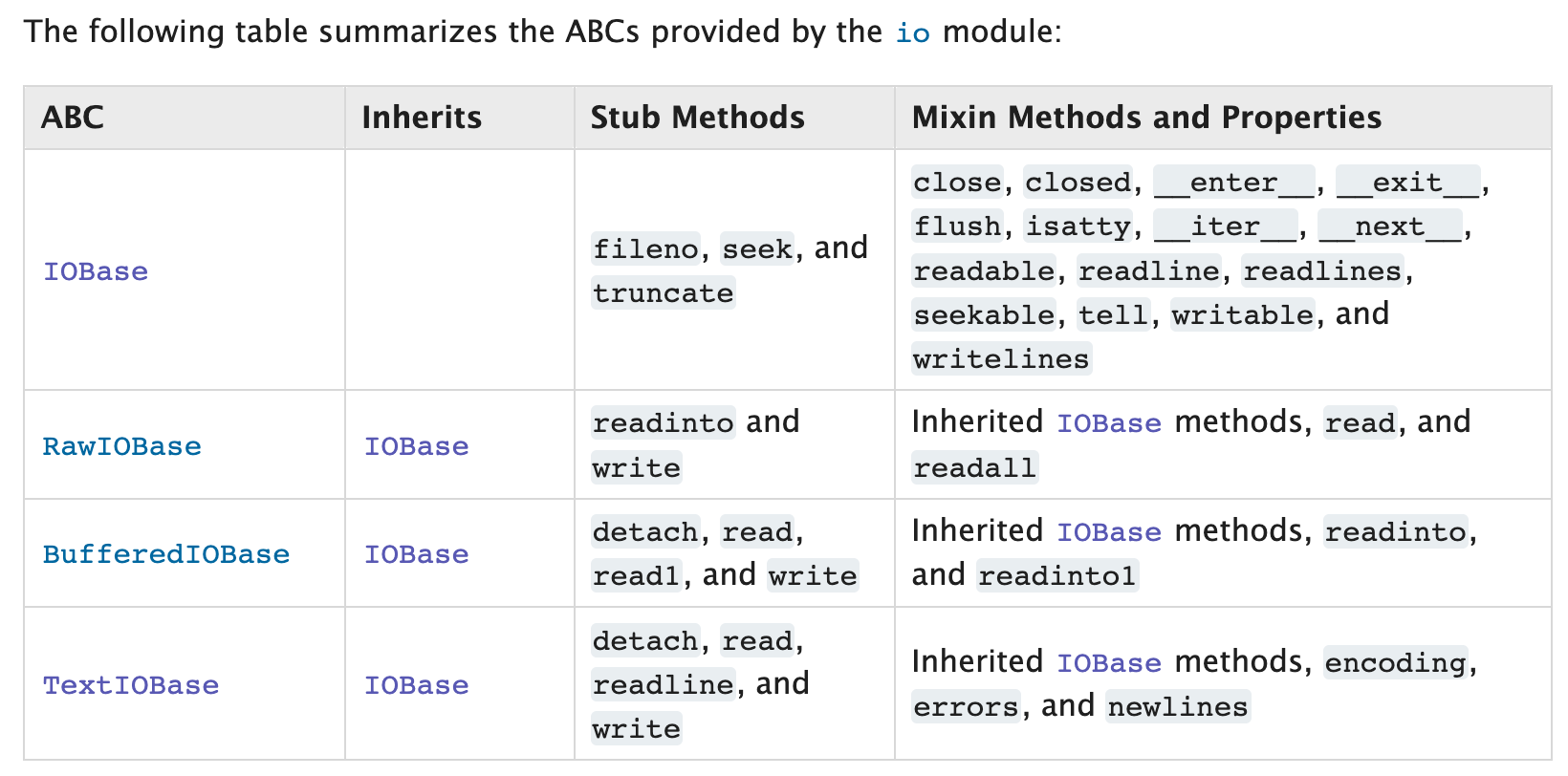
TextIOWrapper의 상속 관계를 따라가보면 TextIOWrapper -> TextIOBase -> IOBase으로 _IOBase class가 최상위에 있다.
IOBase에 __enter__, __exit__함수가 abstract로 선언되어 있음을 할 수 있다.